Infrastructure as Code (IaC) involves managing and provisioning infrastructure through machine-readable definition files, rather than manual configuration. Think of it as applying software development principles – like version control, testing, and automation – to your infrastructure. This allows for consistent, repeatable, and auditable infrastructure deployments across various environments.
The adoption of Infrastructure as Code (IaC) brought immense benefits in terms of speed, consistency, and scalability. However, it also introduced a new attack surface. Misconfigurations or vulnerabilities within IaC templates can lead to widespread security weaknesses in the provisioned infrastructure, potentially impacting numerous resources simultaneously. As organizations increasingly rely on IaC to automate their cloud and on-premises environments, the need to proactively secure these definitions became apparent – hence, the emergence of IaC Security.
What is IaC Security?
IaC Security encompasses the strategies, tools, and practices aimed at identifying, preventing, and mitigating security risks throughout the entire lifecycle of infrastructure defined as code. This includes ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of IaC templates, scanning for misconfigurations and vulnerabilities, enforcing security policies during provisioning, and continuously monitoring the deployed infrastructure for compliance drift. Ultimately, IaC security aims to build secure and resilient infrastructure from the very foundation.
The Need for IaC Security
The paradigm shift towards Infrastructure as Code has revolutionized how organizations provision and manage their digital infrastructure, offering unprecedented speed and consistency. However, this powerful approach introduces a new set of security imperatives. Neglecting the security aspects of IaC can expose organizations to significant risks. Understanding the core reasons why IaC security is paramount is the first crucial step in building a resilient and secure infrastructure in the modern landscape.
Here are the top 6 reasons highlighting the critical need for IaC security
Massive Blast Radius of Misconfigurations
Unlike manual configuration, where errors are often localized, a single security flaw in an IaC template can be replicated across numerous infrastructure components – servers, networks, databases, etc. This “blast radius” means a seemingly small oversight can lead to widespread vulnerabilities and significant security breaches affecting a large portion of the environment simultaneously. For example, an incorrectly configured security group rule in a Terraform template could inadvertently open up critical ports across all newly provisioned web servers.
Shift Left and Early Detection
IaC allows security to be integrated earlier in the infrastructure lifecycle, a core principle of “Shift Left.” By scanning IaC templates before infrastructure is provisioned, organizations can identify and remediate security issues proactively. This is far more efficient and cost-effective than addressing vulnerabilities in running environments, which can involve downtime, rework, and potential security incidents. Imagine detecting an overly permissive IAM role defined in a CloudFormation template before it grants excessive privileges to a service.
Automation and Speed Amplifying Risks
The very benefits of IaC – automation and speed – can also amplify security risks if not managed properly. Flawed IaC code can be deployed rapidly and consistently, propagating vulnerabilities at scale. Without security checks integrated into the automation pipelines, insecure infrastructure can be rolled out quickly across the entire environment, making remediation a much larger and more complex undertaking. Think of an automated pipeline deploying hundreds of virtual machines based on a vulnerable Packer image defined in an IaC template.
Compliance and Governance Enforcement
IaC security provides a mechanism to codify and enforce security policies and compliance requirements directly within the infrastructure definitions. This ensures that provisioned resources adhere to organizational standards and regulatory mandates from the outset. By automating compliance checks within the IaC pipeline, organizations can reduce the risk of non-compliance and ensure consistent adherence to security baselines. For instance, requiring specific encryption settings for all storage accounts defined in ARM templates can be enforced automatically.
Immutable Infrastructure and Drift Detection
IaC often promotes the concept of immutable infrastructure, where changes are made by replacing entire components rather than modifying existing ones. Security becomes an inherent part of the defined infrastructure. Furthermore, IaC security tools can detect configuration drift – unauthorized or unintended changes made to the running infrastructure outside of the IaC definitions. This helps identify potential security compromises or misconfigurations introduced after deployment. Consider a scenario where someone manually opens a port on a server that was supposed to be closed according to the IaC definition; drift detection tools can flag this discrepancy.
Human Error Reduction and Consistency
Manual infrastructure configuration is prone to human error and inconsistencies. IaC, when implemented securely, reduces these risks by codifying the desired state of the infrastructure. This ensures that environments are provisioned consistently and according to defined security specifications, minimizing the chances of human-introduced vulnerabilities. For example, consistently applying network segmentation rules defined in a Terraform module across all application environments reduces the likelihood of accidental misconfigurations.
In conclusion, the need for IaC security is driven by the potential for widespread impact from misconfigurations to the fundamental reduction of human error. By addressing these six key reasons with robust IaC security practices, organizations can harness the power of infrastructure automation without compromising their security posture, ultimately building a more secure and reliable foundation for their applications and services.
What are the challenges and risks associated with implementing IaC Security?
While the benefits of Infrastructure as Code are undeniable, its adoption is not without inherent security challenges and risks. Successfully navigating the complexities of IaC security requires a deep understanding of these potential pitfalls. Addressing these challenges proactively is crucial to realizing the full potential of IaC without compromising the security and integrity of the underlying infrastructure.
Complexity and lack of standardized practices
The IaC landscape is diverse, with numerous tools, platforms, and approaches. This complexity can make it challenging to establish consistent security practices across different environments and technologies. A lack of universally accepted standards and best practices for IaC security can lead to fragmented and inconsistent implementations, increasing the risk of overlooked vulnerabilities and misconfigurations. For instance, securing Terraform configurations might differ significantly from securing Kubernetes manifests, requiring specialized knowledge and tools for each.
Skill gaps and training requirements
Effectively implementing and maintaining IaC security requires a blend of security and infrastructure automation skills. Many organizations face a shortage of professionals who possess this combined expertise. Training existing security and operations teams on IaC concepts, security best practices for specific IaC tools, and integrating security into CI/CD pipelines is a significant undertaking. Without adequately skilled personnel, organizations may struggle to implement robust security controls and may inadvertently introduce vulnerabilities.
”Code Blindness” and False Sense of Security
Teams can sometimes develop a “code blindness” towards their own IaC templates, assuming they are secure because they were written by trusted individuals or have been used before. This can lead to overlooking subtle but critical security flaws. Furthermore, simply adopting IaC tools doesn’t automatically guarantee security. There’s a risk of developing a false sense of security without actively implementing and enforcing security checks and policies within the IaC workflows. For example, teams might assume that using a popular IaC tool inherently provides security without configuring appropriate security scans or reviews.
Integration challenges with existing security tools and processes
Integrating IaC security into existing security toolchains and development workflows can be complex. Traditional security tools might not be designed to analyze IaC configurations effectively, requiring new tools and integrations. Furthermore, adapting existing security processes, such as vulnerability management and incident response, to encompass IaC requires careful planning and execution. Siloed security and operations teams can also hinder effective integration, leading to gaps in coverage.
Secrets Management in IaC
IaC templates often require sensitive information like API keys, passwords, and certificates. Hardcoding these secrets directly into IaC code is a significant security risk. Securely managing and injecting secrets into the infrastructure provisioning process is a critical challenge. Implementing robust secrets management solutions that integrate with IaC workflows, such as HashiCorp Vault or cloud provider secret management services, is essential but can add complexity to the deployment process.
Configuration Drift and Lack of Real-time Visibility
While IaC aims for a defined and consistent state, the deployed infrastructure can still deviate from the IaC configuration due to manual interventions or automated processes outside the IaC pipeline. Detecting and remediating this “configuration drift” is a significant challenge for IaC security. Lack of real-time visibility into the security posture of the provisioned infrastructure and its adherence to the IaC definitions can leave organizations vulnerable to undetected security issues. Implementing continuous monitoring and drift detection mechanisms is crucial but requires additional tooling and integration.
In conclusion, implementing IaC security presents a unique set of challenges, ranging from the complexity of the ecosystem and skill gaps to the critical aspects of secrets management and configuration drift. Recognizing and actively mitigating these risks is important for organizations seeking to leverage the power of IaC securely. By investing in the right expertise, tools, and processes, organizations can overcome these hurdles and build a robust and secure foundation for their automated infrastructure.
What are the top 10 IaC security best practices?
Securing Infrastructure as Code is not merely a suggestion, but a fundamental requirement for building resilient and trustworthy modern infrastructure. The following 10 best practices represent a collection of proven and tested strategies that organizations can adopt to proactively mitigate risks and establish a robust security posture throughout their IaC lifecycle.
- Treat IaC as code with rigorous version control: Employ Git or similar version control systems for all IaC templates. This enables tracking changes, collaborating securely, reverting to previous stable states, and auditing modifications. Every change should be committed, reviewed, and tagged, just like application code.
- Implement comprehensive static analysis: Integrate static code analysis tools specifically designed for your IaC languages (e.g., Cloudanix). These tools can identify misconfigurations, policy violations, and potential security vulnerabilities in your templates before deployment, preventing issues from reaching production.
- Adopt robust secrets management: Never hardcode sensitive credentials in IaC. Utilize dedicated secrets management solutions like HashiCorp Vault, cloud provider secret managers (AWS Secrets Manager, Azure Key Vault, GCP Secret Manager), or even secure parameter stores. Ensure secure access controls and rotation policies for these secrets.
- Enforce the Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP) rigorously: Design IaC templates to provision resources with the absolute minimum permissions required for their function. This applies to IAM roles, security group rules, network policies, and any other access controls defined in your code. Regularly review and refine these privileges.
- Automate security testing in CI/CD pipelines: Integrate security scanning and compliance checks directly into your continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines. This ensures that every IaC change is automatically validated for security issues before being deployed to any environment.
- Implement infrastructure as immutable code: Embrace the concept of immutable infrastructure. Instead of updating existing infrastructure in place, provision new resources with the desired configuration and decommission the old ones. This significantly reduces the attack surface and eliminates configuration drift. IaC makes this approach feasible.
- Establish comprehensive policy enforcement and governance: Define and codify organizational security policies and compliance requirements as code using policy-as-code tools. Integrate these policies into your IaC pipelines to automatically enforce them during provisioning and prevent non-compliant deployments.
- Conduct regular security reviews of IaC templates: Implement mandatory security reviews for all significant IaC changes, similar to code reviews for application development. Involve security engineers in the review process to identify potential security flaws and ensure adherence to best practices.
- Implement continuous monitoring and configuration drift detection: Deploy tools to continuously monitor the deployed infrastructure for any deviations from the defined IaC configuration. Configuration drift can introduce security vulnerabilities. Automated alerts and remediation processes should be in place to address drift promptly.
- Maintain up-to-date IaC tooling and dependencies: Regularly update your IaC tools, providers, and any underlying dependencies. Security vulnerabilities are often discovered and patched in these tools, so keeping them current is crucial for maintaining a secure IaC environment. Track security advisories and apply updates promptly.
By diligently implementing these top 10 security best practices, organizations can significantly enhance the security of their Infrastructure as Code deployments. Embracing these principles will not only minimize the attack surface and reduce the likelihood of misconfigurations but also foster a culture of security within infrastructure automation, ultimately leading to more secure and reliable digital environments.
What are the benefits of IaC Security?
Implementing dedicated security measures for Infrastructure as Code unlocks a range of tangible benefits, transforming how organizations build and manage their infrastructure securely. Here are 6 key benefits that organizations realize specifically after implementing IaC security practices:
Reduced security incidents due to misconfigurations
By proactively scanning IaC templates for security flaws and enforcing policies before deployment, organizations significantly reduce the likelihood of deploying vulnerable infrastructure. This leads to fewer security incidents stemming from common misconfigurations like overly permissive security groups, unencrypted storage, or exposed services.
Faster remediation and lower incident response cost
When security issues are identified early in the IaC lifecycle (Shift Left), remediation is typically faster and less costly. Fixing a misconfiguration in a template is far less disruptive and resource-intensive than patching or re-architecting live, production infrastructure after a security incident.
Improved compliance and auditability
IaC security enables organizations to codify and automatically enforce compliance requirements. This ensures that infrastructure deployments consistently adhere to regulatory standards and internal policies. Furthermore, the version-controlled nature of IaC provides a clear audit trail of infrastructure changes and security configurations, simplifying compliance audits.
Enhanced consistency and standardization of security posture
Implementing security within IaC ensures that security controls are applied consistently across all environments (development, staging, production). This standardization reduces the risk of inconsistent security configurations and strengthens the overall security posture of the organization.
Increased efficiency and velocity in secure deployments
Integrating security into the IaC pipeline (DevSecOps for IaC) automates security checks, eliminating manual and time-consuming security reviews that can bottleneck deployments. This allows development and operations teams to deploy infrastructure changes more rapidly and with greater confidence in their security.
Stronger overall security culture and collaboration
Implementing IaC security often necessitates closer collaboration between security, development, and operations teams. This shared responsibility for infrastructure security fosters a stronger security culture across the organization, where security is considered an integral part of the entire infrastructure lifecycle, not an afterthought.
Ultimately, embracing IaC security not only fortifies infrastructure against threats but also enhances operational efficiency, strengthens compliance, and cultivates a more security-conscious culture within the organization.
How does Infrastructure as Code (IaC) enhance cloud security?
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) enhances cloud security by codifying infrastructure configurations, enabling consistent and repeatable deployments with security baked in. Treating infrastructure like software allows for version control, facilitating auditability and rollback. Automated security scanning of IaC templates identifies misconfigurations early (“Shift Left”). Policy-as-code enforces security standards programmatically. Immutable infrastructure, often provisioned via IaC, reduces the attack surface and configuration drift, leading to a more robust and secure cloud environment.
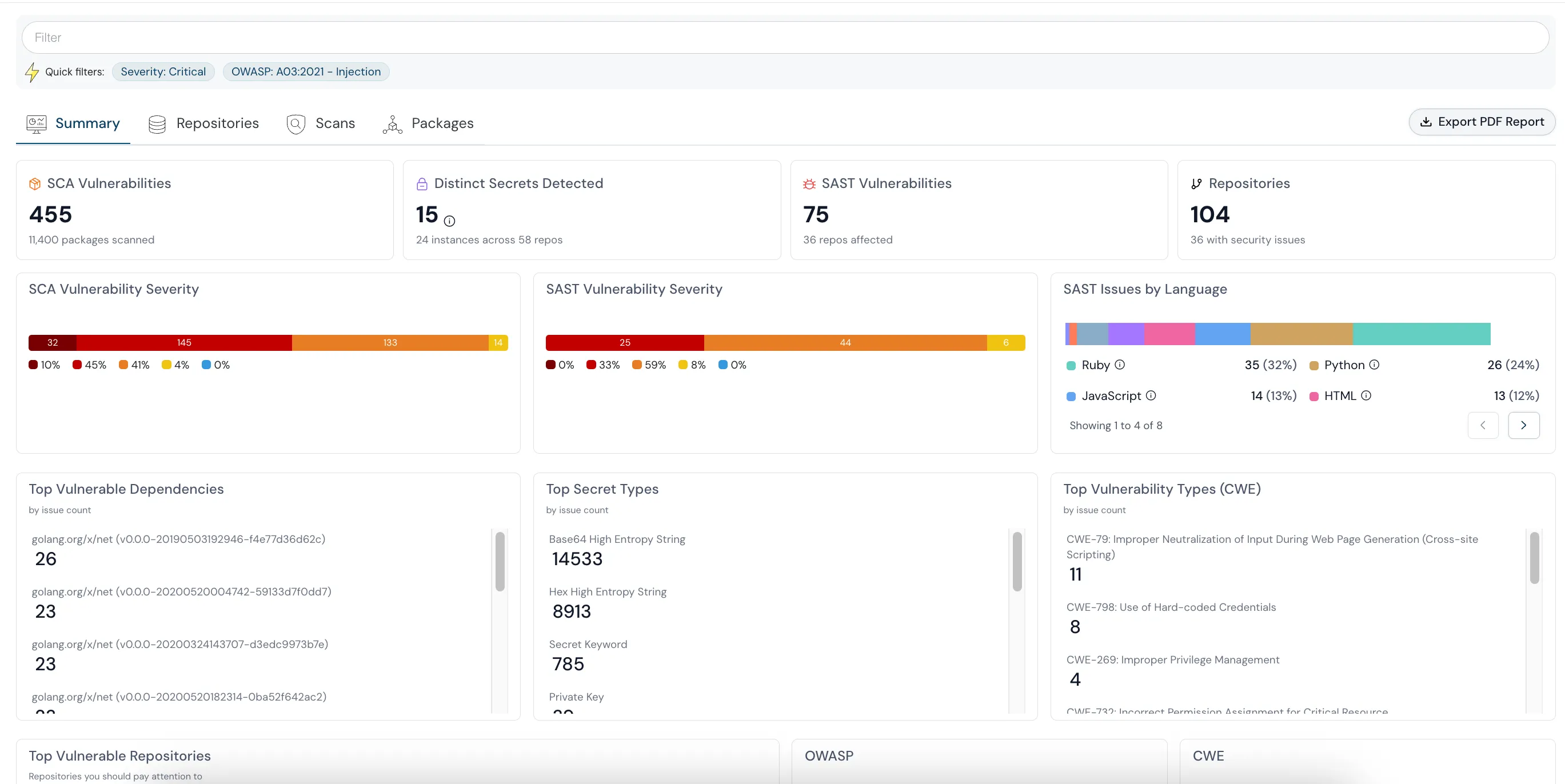
How can Cloudanix help?
A secret exposure, a SAST finding, or an open-source vulnerability must be remediated before it reaches the production environment. Our Shift Left approach ensures that engineering teams get the context and early visibility with a step-by-step remediation playbook during the development cycles. Cloudanix reduces the friction between your developers, security, and ops teams. Integrate with your IaC platform to ensure that you don’t make the same mistakes over and over again.
