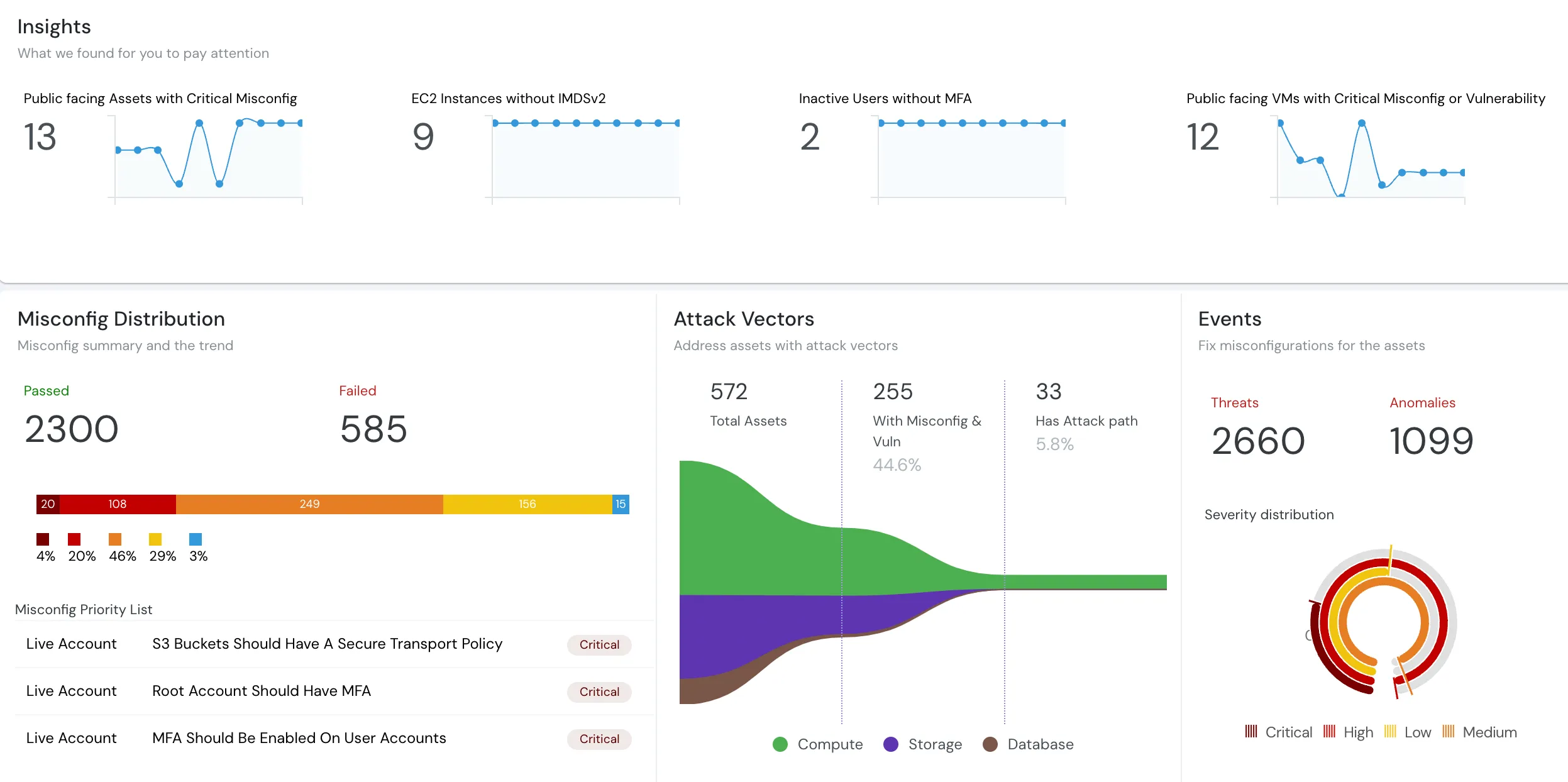
What is a Cloud Audit?
Cloud audit - Comprehensive assessment of cloud environment
Imagine your cloud environment as a house. A cloud audit is like hiring an inspector to check the house for safety, best practices, security, and compliance with building and construction code. The inspector will examine everything from the foundation to the roof, looking for any potential problems or gaps.
Similarly, a cloud audit examines your cloud environment, looking for security vulnerabilities, compliance issues, and overall health. It’s like ensuring that your digital house is safe and secure from potential threats. Pretty easy? Now let us understand the definition and get started!
By definition, a Cloud Audit is a comprehensive assessment of a cloud environment to ensure compliance with regulations, security standards, and organizational policies. It involves a thorough examination of cloud resources, configurations, and user activities to identify potential vulnerabilities, risks, and areas for improvement.
Cloud audits can be performed internally by an organization’s security team or externally by specialized audit firms. They typically involve a combination of manual inspection, automated tools, and interviews with relevant stakeholders. The goal of a cloud audit is to provide a detailed assessment of the cloud environment’s security posture and identify any necessary corrective actions.
What are the different types of cloud audits?
By understanding the different types of cloud audits and their objectives, organizations can make informed decisions about their auditing practices and maintain a secure and compliant cloud environment.
While cloud audits can be categorized based on their specific objectives and scope, we have seen organizations categorize cloud audits into two main categories - Internal Audits and External Audits.
Where Internal audits comprise compliance audits, security audits, and performance audits. External audits include third-party audits, financial audits, and penetration testing. Now let us take a look at each audit type for further understanding.
Compliance audits
- Purpose: To ensure compliance with industry-specific regulations and standards.
- Scope: Varies based on the specific regulations, but typically covers areas such as data privacy, data protection, and record retention.
Security audits
- Purpose: To assess the security posture of the cloud environment and identify potential vulnerabilities.
- Scope: Includes evaluation of access controls, encryption, data protection measures, and compliance with security standards (e.g., ISO 27001, HIPAA, PCI DSS).
Performance audits
- Purpose: To evaluate the performance, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness of cloud services.
- Scope: Includes assessment of resource utilization, performance metrics, and optimization opportunities.
Third-party audits
- Purpose: To provide an independent assessment of the cloud environment by a third-party auditor.
- Scope: Can cover any of the above areas, depending on the specific requirements.
Financial audits
- Purpose: To verify the accuracy and completeness of financial transactions related to cloud services, including billing, usage, and cost allocation.
- Scope: Covers areas such as cost optimization, chargeback mechanisms, and compliance with financial regulations.
Penetration testing
- Purpose: To simulate attacks on the cloud environment to identify vulnerabilities.
- Scope: Includes testing of network security, application security, and data security.
In addition to all of the above, we believe organizations should not overlook the following audit types as well;
Vendor audits
- Purpose: To assess the security practices and compliance of cloud service providers.
- Scope: Includes evaluation of the provider’s security controls, data protection measures, and compliance with relevant regulations.
Operational audits
- Purpose: To assess the effectiveness of cloud operations and processes.
- Scope: Covers areas such as service level agreements (SLAs), disaster recovery planning, and business continuity management.
Risk Assessments
- Purpose: To identify and assess potential risks to the cloud environment.
- Scope: Covers areas such as data breaches, service disruptions, and compliance violations.
In our ScaletoZero podcasts, we were fortunate enough to record an episode with Jeffrey Wheatman, an experienced cybersecurity leader, and practitioner. Jeffrey clearly explained the concept of risk assessment in relation to third-party risk management, vendor audits, and security audits. We recommend taking a look!
What are the benefits of conducting cloud security audits?
Cloud audits offer numerous benefits for organizations of all sizes contributing to improving their overall security posture, compliance, efficiency, etc. Here are some of the key benefits of performing cloud audits:
- Identify vulnerabilities: Cloud audits can help identify and address potential security vulnerabilities, reducing the risk of data breaches and other security incidents.
- Compliance with regulations: By ensuring compliance with industry-specific regulations, cloud audits can help organizations avoid hefty fines and penalties.
- Optimized resource utilization: Performance audits can identify opportunities to optimize resource usage, reducing costs and improving performance.
- Identify Bottlenecks: By identifying performance bottlenecks, organizations can take steps to improve and evolve the overall efficiency of their cloud environment.
- Identify Risks: Cloud audits can help identify potential risks to the cloud environment, allowing organizations to take proactive steps to mitigate them.
- Improve Resilience: By identifying and addressing vulnerabilities, cloud audits can help improve the organization’s resilience to security threats and disruptions.
- Ensure Compliance: Cloud audits can help organizations follow and get compliant with internal policies and procedures.
- Demonstrate Due Diligence: By conducting regular audits, organizations can demonstrate due diligence to stakeholders, customers, and regulators.
- Data-Driven Insights: Cloud audits provide valuable data and insights that can inform decision-making about cloud investments, resource allocation, and risk management.
- Trust and Confidence: By conducting regular audits of cloud service providers, organizations can build trust and confidence in their vendors.
- Negotiation Leverage: Audits can provide valuable information for negotiating on better terms with cloud service providers.
- Avoid Fines and Penalties: Compliance audits can help organizations avoid fines and penalties associated with non-compliance with regulations.
- Cost Optimization: Cloud audits can help organizations identify opportunities to reduce their cloud spending by optimizing resource usage and negotiating better pricing.
What are the 4 As of cloud audits?
Many organizations have claimed about the 4 A auditing framework, even though we tried to gain insights about this framework. It represents a set of best practices and principles that have been developed and refined over time through experience and industry standards.
The concept of ensuring authentication, authorization, accountability, and auditability in IT systems has been around for many years, and its application to cloud environments is a natural extension of these established principles. So, let us provide some insights that we have gathered.
Authentication
- Purpose: To identify and assess potential risks to the cloud environment.
- Scope: Covers areas such as data breaches, service disruptions, and compliance violations.
Authorization
- Purpose: Determines the privileges and permissions granted to users and devices within the cloud environment.
- Key Considerations: Role-based access control (RBAC), least privilege access, and access control lists (ACLs).
Accountability
- Purpose: Ensures that users are held accountable for their actions within the cloud environment.
- Key Considerations: Audit logs, user tracking, and incident response procedures.
Auditability
- Purpose: Enables organizations to track and review user activity, system events, and security incidents.
- Key Considerations: Comprehensive logging, data retention policies, and audit trails.
By addressing these four critical areas, organizations can ensure that they are on the right track to ensure their cloud environments are secure, compliant, and well-governed.
Explain the cloud security audit process
Not just limited to cloud audits, we need to understand that every framework follows a systematic process involving several important steps. In the case of cloud audits, understand it as a collaborative effort between the auditor and the organization that is being audited, with clearly defined roles and policies.
We have tried to explain the process of how to audit cloud environment by categorizing the process into 12 different sections.
1. Defining the Scope and Objectives
- Determine the specific areas to be audited, such as security controls, compliance, performance, or cost-effectiveness.
- Establish clear objectives and goals for the audit.
2. Identify Relevant Standards and Regulations
- Identify industry-specific regulations and standards that apply to your cloud environment (e.g., HIPAA, PCI DSS, GDPR).
- Gather relevant documentation and guidelines.
3. Collect Data and Information
- Gather information about your cloud infrastructure, applications, and user activities.
- Collect relevant logs, configurations, and policies.
4. Assess Security Controls
- Evaluate the effectiveness of your security controls, including access controls, encryption, data protection, and incident response procedures.
- Identify any gaps or weaknesses in your security posture.
5. Review Compliance
- Assess compliance with industry-specific regulations and internal policies.
- Identify any non-compliance issues and develop remediation plans.
6. Evaluate Performance and Cost-Effectiveness
- Analyze resource utilization, performance metrics, and cost efficiency.
- Identify opportunities for optimization and cost reduction.
7. Conduct Penetration Testing
- Simulate attacks on your cloud environment to identify vulnerabilities.
- Assess the effectiveness of your security controls in preventing unauthorized access.
8. Analyze Audit Findings
- Review the audit findings and identify any areas for improvement.
- Prioritize issues based on their severity and potential impact.
9. Develop Remediation Plans
- Create detailed plans to address any identified vulnerabilities or non-compliance issues.
- Assign responsibilities and timelines for remediation efforts.
10. Implement Corrective Actions
- Implement the remediation plans and monitor progress.
- Ensure that corrective actions are effective and address the root causes of identified issues.
11. Document and Report Findings
- Prepare a comprehensive audit report summarizing the findings, recommendations, and corrective actions.
- Share the report with relevant stakeholders, including management, security teams, and compliance officers.
12. Follow-up and continuous monitoring
- Monitor the implementation of corrective actions and ensure ongoing compliance.
- Conduct regular audits to assess the effectiveness of security measures and identify emerging risks.
Even though security is never guaranteed! By following these steps, organizations can conduct effective cloud security audits to identify vulnerabilities, improve their security posture, and ensure compliance with relevant regulations.
What are the three key areas of auditing in cloud environments?
Beyond traditional audit areas, specific aspects of cloud infrastructure require focused attention. By understanding and addressing these key areas, organizations can strengthen their cloud security posture and mitigate risks. Below are the three specific areas to audit when working in cloud environments;
Cloud-native technologies
The rise of cloud-native technologies like containers and serverless functions has transformed the way applications are built and deployed. However, these technologies also introduce new security considerations. Ensuring that cloud-native components are configured securely and protected from vulnerabilities is crucial for maintaining a robust cloud infrastructure. You can get started with the following areas;
- Serverless Functions: Assess the security of serverless functions, including access controls, data isolation, and vulnerability management.
- Container Orchestration: Evaluate the security of container orchestration platforms like Kubernetes and Docker, focusing on areas such as image scanning, network isolation, and privilege escalation prevention.
- Cloud-Native Databases: Examine the security of cloud-native databases, such as NoSQL databases and data warehouses, including data encryption, access controls, and vulnerability management.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Cloud environments, with their unique configurations and shared responsibility models, introduce a new set of security challenges. From misconfigured storage buckets to vulnerable serverless functions, understanding and addressing these cloud-specific vulnerabilities is essential for maintaining a secure cloud environment. Get started with the following IaC areas;
- Configuration Drift: Ensure that IaC templates accurately reflect the desired state of the cloud environment and prevent configuration drift.
- Security Best Practices: Review IaC templates for adherence to security best practices, such as using strong passwords, avoiding hardcoded credentials, and implementing least privilege access.
- Change Management: Evaluate the change management processes for IaC to ensure that changes are properly reviewed, tested, and approved.
Cloud Service Provider (CSP) Security
Building a strong relationship with your cloud service provider (CSP) is essential for effective cloud security. Understanding the shared responsibility model and working closely with your CSP to ensure their security practices align with your organization’s needs can significantly improve your overall security posture. You can get started with the following areas;
- Vendor Assessment: Evaluate the security practices and certifications of your CSP, including compliance with industry standards like ISO 27001 and SOC 2.
- Shared Responsibility Model: Understand the specific security responsibilities shared between your organization and the CSP, and ensure that both parties are meeting their obligations. Read more about Shared Responsibility Model.
- Data Residency and Sovereignty: Assess compliance with data residency and sovereignty requirements, especially if your organization handles sensitive data.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cloud audits are essential for organizations to ensure the security, compliance, and efficiency of their cloud environments. By understanding the different types of cloud audits, their benefits, and the key areas to focus on, organizations can effectively assess their cloud infrastructure, identify vulnerabilities, and take proactive steps to mitigate risks. By conducting regular audits and implementing recommended improvements, organizations can build a strong foundation for secure and compliant cloud operations.
